Exch247, Rock Exchange 9: Cyber insurance is an essential tool for businesses in today’s digital age. It provides financial protection against the increasing threat of cyber attacks and data breaches. By having a cyber insurance policy, companies can mitigate the financial risks associated with potential cyber incidents, such as legal fees, notification costs, data recovery expenses, and potential fines or penalties.
Moreover, cyber insurance typically includes coverage for both first-party and third-party costs. First-party coverage helps companies handle the direct costs resulting from a cyber incident, like forensic investigations, business interruption, and extortion payments. On the other hand, third-party coverage assists with the costs incurred from claims made by customers or partners affected by a data breach, including legal defense fees and settlements. Having comprehensive coverage for both first-party and third-party expenses is crucial for businesses to effectively manage cyber risks.
Types of Cyber Insurance Coverage
Cyber insurance coverage typically includes first-party and third-party coverages. First-party coverage protects against direct losses to the insured organization, such as expenses related to data breaches, ransomware payments, and business interruption costs. It can also encompass forensic investigations to determine the cause of a cyber incident, electronic data restoration, and expenses related to notifying affected individuals.
On the other hand, third-party coverage focuses on liabilities stemming from cyber events that impact others, such as legal defense costs in case of lawsuits, settlements, and regulatory fines. This type of coverage can also extend to coverages for claims related to intellectual property infringement, failure to protect confidential information, and media liability. Understanding the nuances of both first-party and third-party coverages is essential for organizations to ensure comprehensive protection against cyber threats.
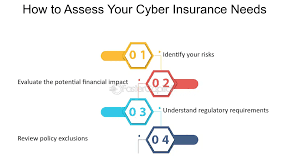
Factors to Consider When Assessing Cyber Risk
When assessing cyber risk, the first crucial factor to consider is the sensitivity and volume of data your organization handles. The more sensitive the data, such as personal or financial information, and the larger the volume, the higher the risk of potential cyber threats. Understanding the value and importance of the data you possess will help in prioritizing security measures.
Another key factor to evaluate is the level of access within your network. Identifying who has access to what data, systems, and networks can help in pinpointing vulnerabilities and potential points of entry for cyber attacks. Limiting access to only those who require it for their roles can reduce the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access. Regularly reviewing and updating access permissions can also strengthen your organization’s cybersecurity posture.
Common Cyber Threats Covered by Insurance
Cyber insurance policies typically cover a wide range of common cyber threats faced by businesses today. One prevalent threat is ransomware, where cybercriminals encrypt a company’s data and demand a ransom for its release. This type of attack can severely disrupt operations and lead to significant financial losses for organizations. With cyber insurance coverage, companies can receive assistance in managing the response to a ransomware attack, including covering the costs of negotiation and potentially the ransom itself.
Another common cyber threat covered by insurance is business email compromise (BEC), where hackers impersonate key personnel within a company to deceive employees into transferring funds or sensitive information. BEC attacks have been on the rise in recent years, leading to substantial financial losses for businesses. Cyber insurance can provide coverage for financial losses resulting from BEC incidents, as well as support for investigating the attack and implementing measures to prevent future occurrences.
• Ransomware is a prevalent cyber threat covered by insurance policies
• Cyber insurance can assist in managing the response to a ransomware attack
• Business email compromise (BEC) attacks are also commonly covered by insurance
• BEC incidents can lead to significant financial losses for businesses
• Cyber insurance can provide coverage for financial losses resulting from BEC attacks
What key aspects should I consider when looking into cyber insurance?
Key aspects to consider when looking into cyber insurance include the types of coverage offered, the limits of coverage, the premiums and deductibles, the reputation and financial stability of the insurance provider, and the specific cyber risks that are covered.
What types of cyber insurance coverage are available?
Common types of cyber insurance coverage include data breach response, cyber extortion, business interruption, network security liability, privacy liability, and regulatory defense and penalties coverage.
What factors should I consider when assessing cyber risk?
Factors to consider when assessing cyber risk include the sensitivity and volume of data stored or processed, the industry and regulatory environment, the reliance on technology systems, the potential impact of a cyber incident on reputation and finances, and the sophistication of potential cyber threats.
What are some common cyber threats covered by insurance?
Common cyber threats covered by insurance include data breaches, ransomware attacks, social engineering scams, DDoS attacks, insider threats, and regulatory fines and penalties resulting from non-compliance with data protection laws.