D247 Login, Peterexch: Data encryption is a process that converts information into a code to prevent unauthorized access. By using advanced algorithms, encryption transforms plain text into a scrambled format, known as ciphertext, which can only be deciphered with the correct decryption key. This security measure ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains incomprehensible to anyone without the appropriate authorization.
In essence, data encryption serves as a protective shield for sensitive information, whether it is being transmitted over networks or stored on devices. This essential security practice safeguards data from prying eyes and malicious actors, offering a crucial layer of defense against unauthorized access and potential breaches. By implementing encryption techniques, organizations can enhance the confidentiality and integrity of their data, reinforcing their cybersecurity posture in an increasingly connected digital landscape.
Types of Encryption Algorithms
Encryption algorithms are essential components of data protection mechanisms, ensuring that information is securely transmitted and stored. One common type of encryption algorithm is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which is widely adopted due to its robust security features and efficiency in encrypting data. AES utilizes symmetric encryption, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, making it a popular choice for securing sensitive information.
Another prevalent encryption algorithm is the Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) algorithm, which is based on asymmetric encryption. RSA involves the use of a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, enhancing the security of data exchanges. This algorithm is commonly used in securing online transactions, digital signatures, and communication protocols to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
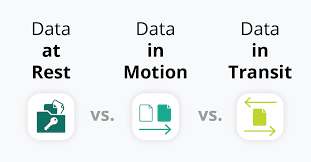
How Does Encryption Protect Data in Transit?
Encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding data during its journey from one point to another over a network. When data is in transit, such as when traveling between servers, devices, or across the internet, it is vulnerable to interception by unauthorized parties. Encryption transforms the original data into an unreadable format, commonly known as ciphertext, using complex algorithms. This process ensures that even if intercepted, the data cannot be deciphered without the proper encryption key.
By utilizing encryption protocols like SSL/TLS, VPNs, and HTTPS, organizations and individuals can establish secure communication channels that protect the integrity and confidentiality of their data during transit. These protocols encrypt data by utilizing symmetric or asymmetric encryption methods, creating a secure tunnel through which information can flow without being compromised. In essence, encryption acts as a virtual shield, preventing cyber attackers from eavesdropping on sensitive data as it travels across networks, thereby maintaining the privacy and security of the information being transmitted.
Securing Data at Rest with Encryption
Data encryption plays a crucial role in securing data at rest by scrambling the information in storage, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. By converting plaintext data into ciphertext using mathematical algorithms and encryption keys, sensitive information remains protected even if the storage device is compromised.
Implementing encryption for data at rest helps organizations comply with data protection regulations and safeguard against potential data breaches. Through strong encryption techniques, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) or Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES), businesses can ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their stored data, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and unauthorized tampering.
• Data encryption scrambles information in storage
• Converts plaintext data into ciphertext using algorithms and keys
• Protects sensitive information even if storage device is compromised
Implementing encryption for data at rest:
• Helps organizations comply with data protection regulations
• Safeguards against potential data breaches
• Ensures confidentiality and integrity of stored data
Strong encryption techniques:
• Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
• Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES)
• Mitigates risk of unauthorized access and tampering
What is data encryption?
Data encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. This code can only be deciphered with the use of a decryption key.
What are some common types of encryption algorithms?
Some common types of encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), RS
How does encryption protect data in transit?
Encryption protects data in transit by encoding the information so that it cannot be intercepted and read by unauthorized parties. This is commonly used in securing communications over the internet.
How can encryption help secure data at rest?
Encryption helps secure data at rest by converting the information into a code that can only be accessed with the correct decryption key. This prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data stored on devices or servers.