As humanity grapples with the escalating consequences of climate change, one of the most pressing concerns is its profound impact on biodiversity. From the poles to the tropics, ecosystems around the globe are facing unprecedented challenges as temperatures rise, weather patterns shift, and habitats undergo profound transformations.
1. Understanding Biodiversity: Biodiversity encompasses the staggering variety of life forms on Earth, from microscopic organisms to majestic mammals. Ecosystems thrive on biodiversity, relying on the intricate interactions between species to maintain balance and resilience.
2. Climate Change and Habitat Loss: One of the most significant threats to biodiversity is habitat loss, driven primarily by human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and industrial agriculture. Climate change exacerbates this threat by altering temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to shifts in vegetation zones and the loss of critical habitats.
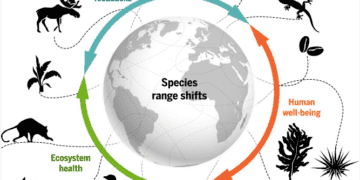
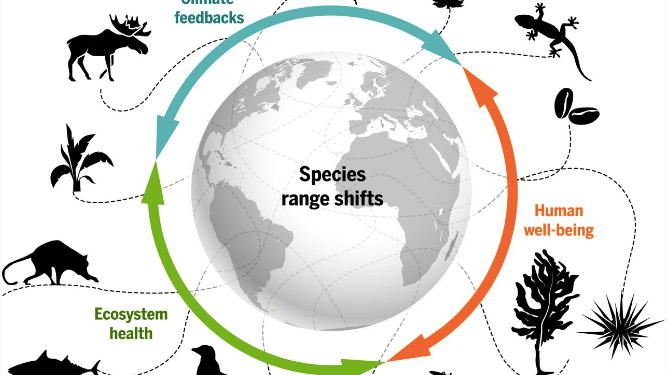
3. Disruption of Ecosystem Dynamics: Climate change disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, triggering cascading effects throughout food webs and ecological communities. As temperatures rise, species may be forced to migrate in search of suitable habitats, leading to competition for resources and potential conflicts with native species.
4. Threats to Keystone Species: Keystone species play a critical role in maintaining the structure and function of ecosystems, exerting disproportionate influence on their surroundings. Climate change poses significant threats to keystone species such as apex predators, large herbivores, and foundation species, which are particularly sensitive to environmental changes.
5. Conservation Strategies in a Changing Climate: Addressing the impact of climate change on biodiversity requires a multifaceted approach that integrates conservation efforts, policy interventions, and community engagement. Conservation strategies may include the establishment of protected areas, habitat restoration initiatives, and the implementation of sustainable land management practices.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the impact of climate change on biodiversity represents a profound challenge that requires urgent and concerted action at local, national, and global levels. Protecting biodiversity is not only essential for the health and resilience of ecosystems but also for the well-being of humanity and future generations. By recognizing the interconnectedness of all life forms and embracing our role as stewards of the planet, we can work together to mitigate the impact of climate change and safeguard the rich tapestry of life that sustains us all.